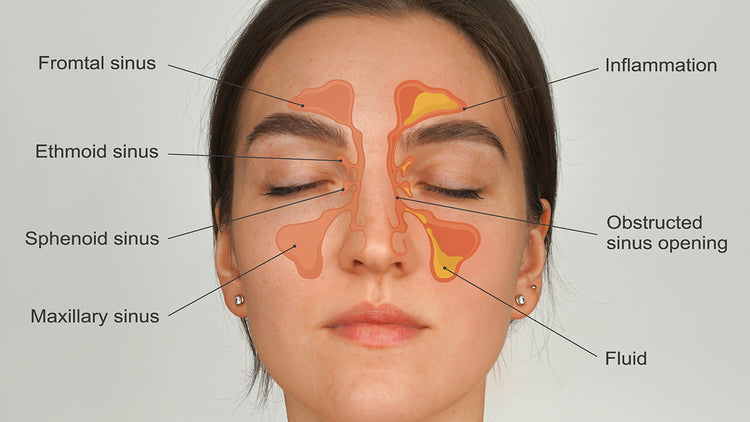
A sinus infection or sinusitis is an inflammation of the tissues in your sinuses, which are the cavities in the nose, forehead, and cheeks that are usually filled with air. The common cold typically causes sinus infections. Other viruses, bacteria, fungi, and allergens can also cause sinus infections. Sinusitis may warrant treatment medications, whether antibiotics or over-the-counter medications. The type of medication needed will depend on the type of infection, severity, and other factors. Below we will discuss treatment options and how you can expect to feel during days one to three on sinus medication.
What Are the Potential Side Effects of Taking Sinus Medication?
A sinus infection can cause various symptoms, such as fever, facial pain, headaches, and a stuffy nose or nasal congestion. Over-the-counter medications used to treat sinusitis may include decongestants and pain relievers. Oral decongestants, such as Sudafed, work by tightening the blood vessels in the nose, lessening swelling, and making it easier to breathe through the nose again. These medications can cause side effects, such as trouble sleeping, anxiety, sweating, and a temporary increase in heart rate and blood pressure.
There are additional considerations if you take an over-the-counter pain medication, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen. For example, patients with certain medical conditions such as heart disease or high blood pressure; gastrointestinal upset or peptic ulcers; or kidney, liver, or heart disease should speak to their healthcare provider before taking any OTC pain relievers as they may further exacerbate their conditions.
If antibiotic usage is indicated for a sinus infection, some side effects are important to look out for. Side effects may be mild and include things like a rash or something more serious like antibiotic-resistant infections, severe allergic reactions, and C. diff infection. The antibiotic for sinus infection treatment is typically amoxicillin or Augmentin. If you have a penicillin allergy, you can take Doxycycline.
How Should I Feel on Days 1-3 of Sinus Medication?
After beginning treatment for a sinus infection, you may wonder how long it will take before you start feeling better. If you take an antibiotic for a suspected bacterial infection, most patients begin to see relief within three to four days of starting the medication. If you take an over-the-counter decongestant or pain reliever, healthcare professionals generally recommend that you not take these longer than three days without seeking guidance from a medical provider. If your sinus infection symptoms last longer than ten days without improvement, you should make an appointment to see your healthcare provider, as you may require a prescription for treatment or have another infection occurring concurrently, such as strep throat.
What Should I Do If I Experience Any Adverse Reactions to the Medication?
If you experience an adverse reaction to any medication, you should first stop taking it and contact your healthcare provider. Some adverse reactions and complications may occur when you take the medication with other prescribed or non-prescribed medications. You should stop the medicine and contact your healthcare provider if you experience any allergic reaction, such as skin rash, itching, hives, or swelling of the lips, tongue, face, or throat.
Other reactions that you should report to your healthcare provider include heart palpitations (a rapid, irregular, pounding heartbeat) and increased blood pressure. If you ever have a question about a side effect or reaction, always contact your medical provider or a pharmacist. Always ensure that your healthcare provider has an up-to-date and accurate list of current medications you are taking and medical conditions so they can properly recommend medication and prescribe any antibiotics needed.
How Long Will It Take for the Sinus Medication to Take Effect?
Over-the-counter oral decongestants work fairly quickly. You can expect them to take effect within 30-60 minutes after taking the first dose. Relief from symptoms may continue from 4 to 24 hours after you take the medication, depending on which medication you take. If you take an antibiotic for a bacterial sinus infection treatment, you will usually start to see relief from symptoms within two to four days of initiating antibiotic therapy. You can also take antihistamines to help combat symptoms. They work by blocking histamine in the body. Too much histamine in the body can cause symptoms such as stuffiness, coughing, and nasal discharge.
While waiting for the medication to take effect, there are some home remedies you can start to help with symptom relief. These may include the following:
- Using a warm compress on the sinus area to help relieve sinus pressure
- Breathing in the steam from a hot shower or a bowl of hot water
- Using a saline nose spray
Is There a Recommended Dosage of Sinus Medication That I Should Adhere to?
The recommended dosage of medication will vary from patient to patient. Various factors go into recommended dosages, such as the age and weight of the patient. Healthcare professionals recommend that you follow package instructions or instructions provided by your pharmacist or medical provider when taking medication. If you miss a dose of medicine, you should take it as soon as possible. However, if it is almost time for your next dose, you should skip the missed dose and return to your regular dosing schedule.
You can easily manage sinusitis, or a sinus infection, with the correct interventions and medications. Finding the proper treatment for symptom management and an antibiotic, if warranted, should help clear up symptoms reasonably quickly. Since viruses and bacteria often cause sinus infections, it is essential to thoroughly clean the household and common touch areas after treatment to ensure others do not get sick. If symptoms do not improve within five to ten days after initiating medication, it is crucial to consult your healthcare provider for further guidance.
References
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2019, Aug 27). Sinus infection (sinusitis). https://www.cdc.gov/antibiotic-use/sinus-infection.html#:~:text=Side%20effects%20can%20range%20from,infections%20and%20C.%20diff%20infection
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022, Sept 7). What is c. diff? https://www.cdc.gov/cdiff/what-is.html.
Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Pseudoephedrine capsules and tablets. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/drugs/20768-pseudoephedrine-capsules-and-tablets
Cleveland Clinic. (2023, Mar 9). Sinus infection (sinusitis). https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17701-sinusitis
Kaiser Permanente. (2023, Mar 1). Sinusitis: should I take antibiotics? https://healthy.kaiserpermanente.org/health-wellness/health-encyclopedia/he.sinusitis-should-i-take-antibiotics.zx3953.
Mayo Clinic. (2023, May 1). Pseudoephedrine (oral route). https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements/pseudoephedrine-oral-route/proper-use/drg-20067942
Smedley, T. (2022, June 28). What are the best over-the-counter options for sinus infections?. GoodRX Heath. https://www.goodrx.com/conditions/sinus-infection/best-otc-sinus-infection
Thomas, S.A. (2022, Aug 8). How long can you take oral decongestants like sudafed?. GoodRX Heath. https://www.goodrx.com/conditions/cold-symptoms/how-long-take-oral-decongestants-sudafed

Nurse Bio
Lauren is a Registered Nurse with 8+ years of nursing experience. She received her bachelor's degrees in Communication Studies and Nursing as well as a Master's degree in Business Administration. She has nursing experience in pediatrics, rehabilitation and, most recently, clinical informatics. She has a passion for taking her real-life experience and expertise and transforming it into content that the general public can understand and digest.
Life is too short to sit in a doctor’s office
Sign up for our weekly newsletter and get valuable healthcare tips and tricks in your inbox!
Sign up now and unsubscribe anytime.
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Press the space key then arrow keys to make a selection.